1、从远程库clone
git clone ssh://…
2、提交
把文件修改添加到暂存区
git add <path-to-file>
把暂存区的所有内容提交到当前分支
git commit -m “xxx”
推送到远端仓库
git push <远程主机名> <local-branch>:<remote-branch>
3、分支管理(branch)
查看分支
git branch -a
创建分支
git branch <name>
切换分支
git checkout <name>
创建+切换分支
git checkout -b <name>
合并某分支到当前分支
git merge <name>
删除分支
git branch -d <name>
git branch -D <name>
本地分支重命名
git branch -m <old> <new>
拉取远程分支并创建本地分支
git checkout -b <name> origin/<name>
4、版本回退
HEAD指向的版本就是当前版本,因此,Git允许我们在版本的历史之间穿梭,使用命令:
git reset --hard <commit_id>
- 穿梭前,用git log可以查看提交历史,以便确定要回退到哪个版本。
- 要重返未来,用git reflog查看命令历史,以便确定要回到未来的哪个版本。
5、撤销修改
场景1:当你改乱了工作区某个文件的内容,想直接丢弃工作区的修改时,使用命令:
git checkout -- <path-to-file>
场景2:当你不但改乱了工作区某个文件的内容,还添加到了暂存区时,想丢弃修改,分两步,第一步用命令:
git reset HEAD <path-to-file>
就回到了场景1,第二步按场景1操作。
场景3:已经提交了不合适的修改到版本库时,想要撤销本次提交,参考版本回退一节,不过前提是没有推送到远程库。
6、查看日志(log)
git log --graph --pretty=oneline --abbrev-commit
git log --graph --pretty=format:”%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset” --abbrev-commit --date=relative
7、比较文件差异(diff)
工作目录 vs 暂存区
git diff <path-to-file>
查看和另一分支的区别:
git diff <branch> <path-to-file>
暂存区 vs Git仓库
git diff --cached <path-to-file>
指定仓库版本:
git diff --cached <commit> <path-to-file>
工作目录 vs Git仓库
git diff <commit> <path-to-file>
Git仓库 vs Git仓库
git diff <commit1> <commit2> <path-to-file>
使用vimdiff工具进行比较
git difftool --tool=vimdiff <path-to-file>
或者先配置:
git config --global diff.tool vimdiff
git config --global difftool.prompt false
再进行比较:
git difftool <path-to-file>
Note:也可以直接修改配置文件~/.gitconfig
8、合并(merge)
当前本地分支和远程分支merge
git merge <remote-host>/<remote-branch>
git mergetool
使用vimdiff作为冲突解决的工具
配置使用vimdiff工具进行merge:
git config --global merge.tool vimdiff
git config --global mergetool.prompt false
解决冲突
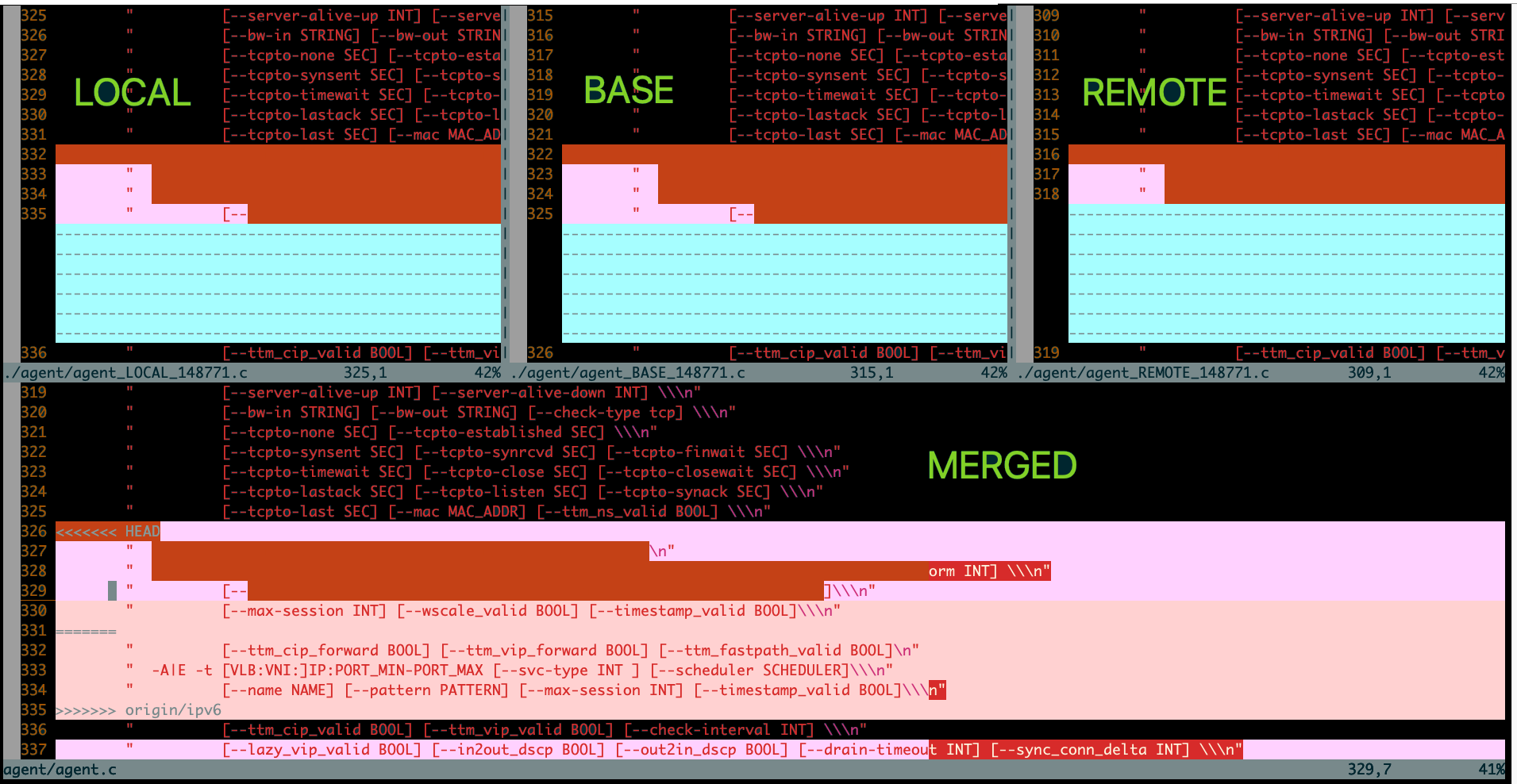
- LOCAL:这个文件来自当前分支;
- BASE:两个分支的共同祖先,在两个分支上的文件改变之前的样子;
- REMOTE:要合并到你当前分支的外部分支上的文体;
- MERGED:合并结果,将会保存到本地repo中。
假如我们希望保留来自REMOTE的变化,为此移动到MERGED文件上,移动光标到一个合并冲突的区域,然后执行:
:diffget RE
这一步从REMOTE上获得相应的更改并将其放入到MERGED文件中,也可以执行:
:diffget RE
:diffget BA
:diffget LO
9、rebase
当前本地分支和远程分支rebase
git rebase <remote-host>/<remote-branch>
git rebase --continue
在任何时候,你可以用--abort参数来终止rebase的行动,并且本地 分支会回到rebase开始前的状态。
git rebase --abort
10、fetch
一旦远程主机的版本库有了更新(Git术语叫做commit),需要将这些更新取回本地,这时就要用到git fetch命令。
git fetch <remote-host>
git fetch <remote-host> <remote-branch>
其它相关命令
| 查看远程分支 | git branch -r |
| 查看所有分支 | git branch -a |
| 查看本地分支和远程分支的对应关系 | git branch -vv |
| 在远程分支基础上创建一个新的分支 | git checkout -b <local-branch> <remote-host>/<remote-branch> |
| 在本地分支上合并远程分支 | git merge <remote-host>/<remote-branch> git rebase <remote-host>/<remote-branch> |
11、pull
git pull命令的作用是,取回远程主机某个分支的更新,再与本地的指定分支合并。
git pull <remote-host> <remote-branch>:<local-branch>
如果远程分支是与当前分支合并,则冒号后面的部分可以省略。
git pull <remote-host> <remote-branch>
在某些场合,Git会自动在本地分支与远程分支之间,建立一种追踪关系(tracking)。比如,在git clone的时候,所有本地分支默认与远程主机的同名分支,建立追踪关系,也就是说,本地的master分支自动”追踪”origin/master分支。
Git也允许手动建立追踪关系。
git branch --set-upstream-to <remote-host>/<remote-branch> <local-branch>
如果当前分支与远程分支存在追踪关系,git pull就可以省略远程分支名。
git pull <remote-host>
如果当前分支只有一个追踪分支,连远程主机名都可以省略。
git pull
如果合并需要采用rebase模式,可以使用-–rebase选项。
git pull --rebase <remote-host> <remote-branch>:<local-branch>
12、push
git push命令用于将本地分支的更新,推送到远程主机。它的格式与git pull命令相仿。
git push <remote-host> <local-branch>:<remote-branch>
如果省略远程分支名,则表示将本地分支推送与之存在”追踪关系”的远程分支(通常两者同名),如果该远程分支不存在,则会被新建。
git push <remote-host> <local-branch>
如果省略本地分支名,则表示删除指定的远程分支,因为这等同于推送一个空的本地分支到远程分支。
git push <remote-host> :<remote-branch>
如果当前分支与远程分支之间存在追踪关系,则本地分支和远程分支都可以省略。
git push origin
如果当前分支只有一个追踪分支,那么主机名都可以省略。
git push
13、储藏(stash)
为了往堆栈推送一个新的储藏,只要运行:
git stash
要查看现有的储藏,可以使用:
git stash list
重新应用刚才实施的储藏,可以使用:
git stash apply
如果想应用更早的储藏,可以通过名字指定它:
git stash apply stash@{2}
对文件的变更被重新应用,但是被暂存的文件没有重新被暂存。想那样的话,你必须运行
git stash apply --index
来告诉命令重新应用被暂存的变更。
apply 选项只尝试应用储藏的工作——储藏的内容仍然在栈上。要移除它,你可以运行git stash drop,加上你希望移除的储藏的名字:
git stash drop stash@{0}
你也可以运行git stash pop来重新应用储藏,同时立刻将其从堆栈中移走。
在某些情况下,你可能想应用储藏的修改,在进行了一些其他的修改后,又要取消之前所应用储藏的修改。Git没有提供类似于stash unapply的命令,但是可以通过取消该储藏的补丁达到同样的效果:
git stash show -p stash@{0} | git apply -R
git stash show -p | git apply -R
从储藏中创建分支
git stash branch <branch-name> stash@{0}
带消息的git stash
git stash save “Your stash message”
14、补丁(patch)
生成patch
两个commit间的修改(包含两个commit)
git format-patch <commit1>..<commit2>
单个commit
git format-patch -1 <commit1>
从某commit以来的修改(不包含该commit)
git format-patch <commit1>
测试patch
检查patch文件
git apply --stat 0001-minor-fix.patch
查看是否能应用成功
git apply --check 0001-minor-fix.patch
应用patch
git am -s < 0001-minor-fix.patch
15、cherry-pick
git cherry-pick可以选择某一个分支中的一个或几个commit(s)来进行操作。例如,假设我们有个稳定版本的分支,叫v2.0,另外还有个开发版本的分支v3.0,我们不能直接把两个分支合并,这样会导致稳定版本混乱,但是又想增加一个v3.0中的功能到v2.0中,这里就可以使用cherry-pick了,其实也就是对已经存在的commit 进行再次提交。
git cherry-pick -e <commit>
-e选项允许在commit前修改提交信息,不加-e选项的话提交信息就和原来一致。 如果提示出现冲突,则可以使用:
git mergetool
git commit -c <commit>